In a study published in Nucleic Acids Research on May 19, entitled “mRNAdesigner: an integrated web server for optimizing mRNA design and protein translation in eukaryotes,” Professor HAO Pei from the Shanghai Institute of Immunity and Infection (SIII) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, introduced mRNAdesigner, an open-access web-based platform for mRNA drug design. This achievement represents a major advancement in the customized design and efficient development of next-generation mRNA-based nucleic acid therapeutics, accelerating academic research and reducing barriers to industrial application.
mRNA therapeutics have emerged as a key frontier in modern biomedicine. However, current mRNA design is hindered by several challenges, including limited cross-species adaptability, insufficient consideration of the regulatory roles of untranslated regions (UTRs), and inadequate control over immunogenicity. To tackle these issues, Professor HAO’s team integrated insights from RNA translational dynamics into their design framework. The platform considers multiple critical factors, such as codon usage bias, GC content, and mRNA secondary structure, to optimize three major structural regions of mRNA: the 5′ untranslated region (5′UTR), coding sequence (CDS), and 3′ untranslated region (3′UTR).
For the CDS, the platform enables optimization under user-defined GC content levels, improving the codon adaptation index (CAI), refining base-pairing patterns, and minimizing the formation of long stem-loop structures and GC-rich regions. These improvements reduce the likelihood of recognition and degradation by the innate immune system. For the 5′UTR, the optimization strategy boosts the mean ribosome load (MRL), thereby enhancing translation initiation and elongation efficiency. In the 3′UTR, a regulatory element annotation algorithm is employed to identify and minimize sequence motifs associated with mRNA degradation (e.g., AREs, CUREs), improving both stability and translational output.
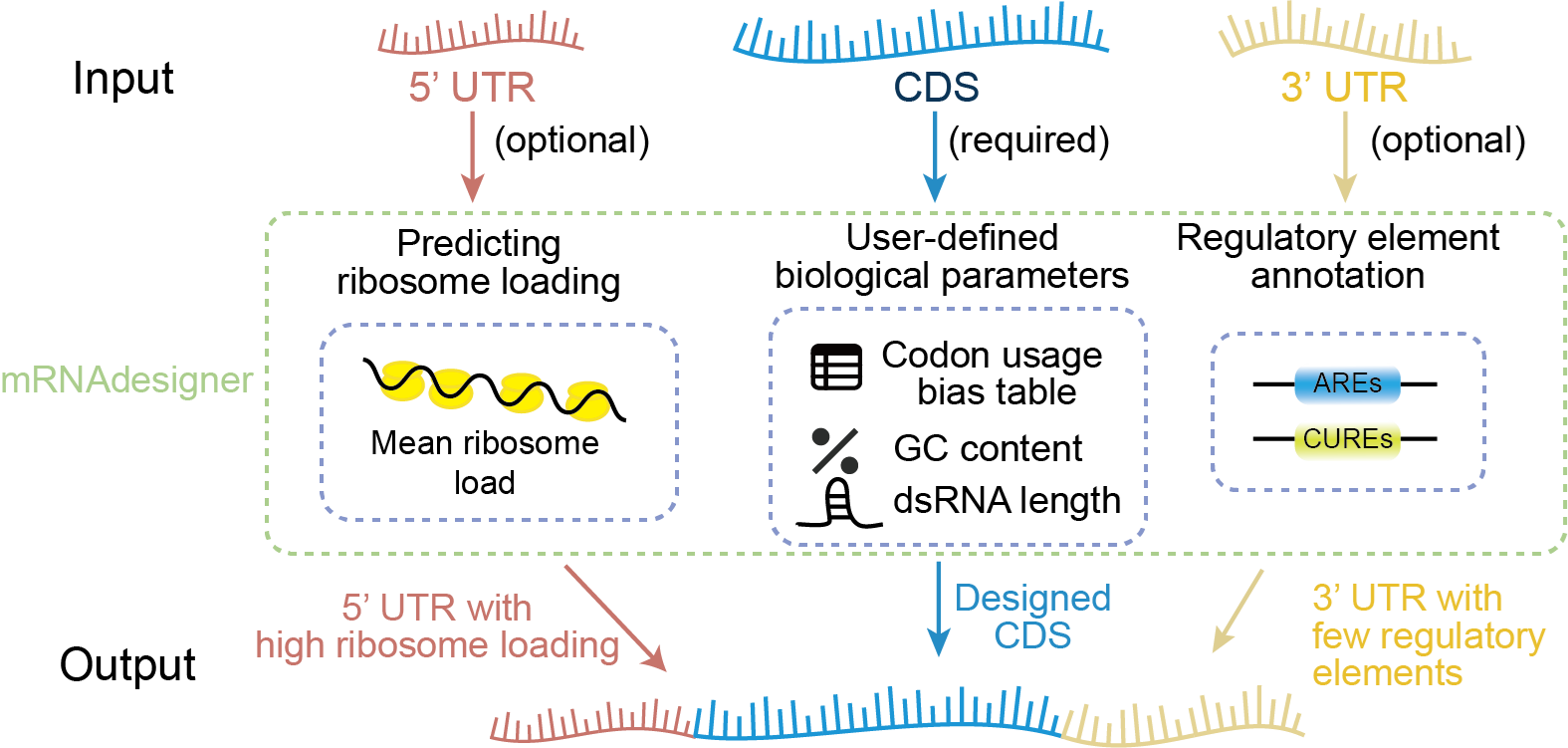
Figure1: Schematic Diagram of mRNAdesigner Sequence Optimization Workflow. (Image by SIII)
Simulations and experimental validations have shown that mRNA sequences designed using mRNAdesigner outperform their original counterparts in codon adaptation, base-pairing accuracy, and reduction of detrimental secondary structures. Additionally, the optimized sequences exhibit significantly higher protein expression levels in eukaryotic systems. The platform provides strong support for the development of nucleic acid vaccines, protein therapeutics, and broader applications in molecular biology research.
mRNAdesigner is available at https://www.biosino.org/mRNAdesigner/ .
Contact:
HAO Pei
Shanghai Institute of Immunity and Infection, Chinese Academy of Sciences
phao@siii.cas.cn
Reference: https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkaf410

